Building a team is one of the most critical aspects of running a successful business, often raising a pivotal question: Should you hire a freelancer or commit to a full-time employee? This decision is far more complex than merely weighing costs or convenience. It profoundly impacts your company’s productivity, operational efficiency, team dynamics, and long-term growth. Freelancers and full-time employees each offer unique advantages, but they also come with challenges that influence the way your organization functions. From determining how work gets done to the quality of output and the relationships built within your team, this decision shapes not only your business’s adaptability to market changes but also its ability to sustain growth over time.
Choosing a freelancer may provide flexibility, cost savings, and access to specialized talent, but it could lead to challenges in team collaboration and continuity. On the other hand, full-time employees foster loyalty, cultural alignment, and consistent availability, though they come with higher financial commitments and reduced agility. By thoroughly evaluating the advantages, limitations, and ideal use cases of each model, businesses can avoid costly mistakes and build a workforce tailored to their goals and operational needs. This decision goes beyond simply filling roles—it’s about creating a team that drives innovation, efficiency, and long-term success.

In this guide, we’ll explore the nuances of both freelance and full-time hiring models, offering actionable insights, real-world examples, and a touch of humor—because let’s face it, hiring doesn’t have to be boring. Whether you’re a startup founder, hiring manager, or CTO, this article is for you. Let’s dive into the great hiring debate!
The Fundamentals of Freelance and Full-Time Hiring
Before we compare, let’s define what sets freelancers apart from full-time employees:
Freelancers are independent contractors hired on a project or hourly basis, offering businesses flexibility and access to specialized skills without long-term commitments. They often work for multiple clients simultaneously, making them ideal for short-term projects or tasks requiring niche expertise. While freelancers provide cost-effective solutions, their availability and focus can be divided, which may limit their integration into a company’s culture and workflows. Despite this, they remain a valuable option for businesses seeking agility and quick results.
Full-Time Employees are permanent staff members who work exclusively for your organization under a formal employment contract. They typically follow fixed working hours and receive benefits such as health insurance, paid leave, and retirement plans. Full-time employees are deeply integrated into the company’s operations and culture, offering consistency and long-term commitment. While they provide reliability and foster team collaboration, they come with higher costs and less flexibility compared to freelancers.
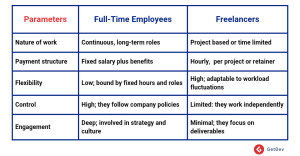
Freelancing has gained significant traction due to the rise of remote work and gig platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, and Toptal. However, full-time employment remains essential for roles requiring deep integration with your company’s goals and culture.
Stability and Long-Term Vision; Full-Time Employment
Full-time employees are the cornerstone of most organizations. They offer consistency, stability, and a deep understanding of your business, making them indispensable for long-term success.
Key Benefits
1.Cultural Integration: Full-time employees align closely with your company’s culture, fostering collaboration and a shared vision.
2.Consistency: Their predictable availability ensures reliability for ongoing operations.
3.Loyalty and Retention: Providing career growth opportunities and benefits encourages long-term commitment.
Challenges
- Higher Costs: Salaries, benefits, and taxes make full-time employees a more expensive option.
- Limited Flexibility: Scaling your workforce during market fluctuations can be slow and costly.
- Time-Consuming Onboarding: Recruitment and training require significant time and resources.
Best Use Cases for Full-Time Employees
- Long-term projects requiring consistent attention.
- Roles demanding strong collaboration with internal teams.
- Industries that prioritize talent retention, like healthcare or software development.
Agility and Expertise on Demand; Freelance Model
Freelancers provide unparalleled flexibility, allowing businesses to access specialized skills for specific projects without long-term commitments.
Key Benefits
1. Cost-Effectiveness: Freelancers are paid per project or hourly, eliminating expenses like benefits and pensions.
2. Flexibility: Quickly scale your workforce up or down based on project needs.
3. Access to Specialized Talent: Freelancers often possess niche expertise that may not be available in-house.
Challenges
- Limited Availability: Freelancers may not always be available for future projects.
- Lower Commitment: Their focus is divided across multiple clients.
- Potential Integration Issues: Freelancers may lack familiarity with company workflows or culture.

Best Use Cases for Freelancers
- Short-term projects with clear deliverables.
- Tasks requiring specialized skills, like graphic design or SEO optimization.
- Businesses with fluctuating workloads or seasonal demands.
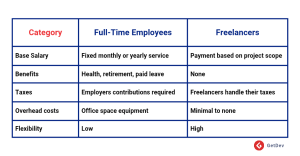
A Comparison of Costs: Freelance vs. Full-Time
Freelancers are often the cost-effective choice for short-term projects, while full-time employees provide better ROI for long-term roles. Here’s how freelancers and full-time employees compare from a financial perspective:
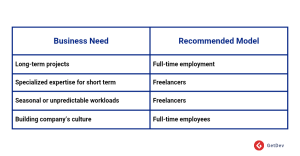
Decision Framework: Freelance, Full-Time, or Both?
A balanced workforce that combines the agility of freelancers with the stability of full-time employees can be a game-changer for businesses. Whether you’re managing long-term initiatives or responding to seasonal demands, this hybrid model offers flexibility while ensuring consistent quality. Here’s how to decide:
For maximum impact, consider combining both models. For example:
- A tech startup might hire full-time developers for core functions while engaging freelance UX designers for short-term projects.
- •An e-commerce business could maintain a full-time operations team while onboarding freelance customer service agents during peak shopping seasons.
Practical Considerations for Implementation
- Define Clear Roles: Specify which tasks require full-time commitment and which can be outsourced.
- Use Technology: Leverage tools like Trello or Slack for seamless collaboration between freelancers and full-time staff.
- Prioritize Communication: Ensure clear expectations and regular updates to align everyone with company goals.
- Legal Compliance: Draft clear contracts for freelancers and comply with local employment laws
Conclusion
The choice between freelancers and full-time employees ultimately depends on your business goals, budget, and project needs. While freelancers offer flexibility and specialized expertise, full-time employees bring stability and cultural alignment.
By assessing your priorities and adopting a strategic mix of both models, you can create a workforce that drives innovation, efficiency, and growth. So, ask yourself:
- Is the task ongoing or one-off?
- Does it require deep team collaboration?
- What’s my budget?
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution, but with the right balance, you can build a team that sets your business up for success.